百万级数据量导出EXCEL解决方案分析
1. 问题概述 在web页面上显示的报表导出到excel文件里是一种很常见的需求, 润乾报表的类excel模型,支持excel文件数据无失真的导入导出, 然而,当数据量较大的情况下,就会遇到一些问题: 1. 2003Excel本身的支持最多65535行数据 2. 在这种大数据量的报表生成和导出中,要占用大量的内存,甚至内存溢出 难点:1.数据量大,报表在运算成ireport对象时每个sheet页内存不释放,可能内存溢出. 2.即使能够运算完ireport对象再导出Excel的过程中内存不释放,可能内存溢出.
2 . 案例 上海期货交易所 上海唯智信息
3. 解决方案 一. 对于数据超过了65535行的问题,很自然的就会想到将整个数据分块,利用excel的多sheet页的功能,将超出65535行后的数据写入到下一个sheet页中,即通过多sheet页的 方式,突破了最高65535行数据的限定, 具体做法就是,单独做一个链接,使用JSP导出,在JSP上通过程序判断报表行数,超过65535行后分SHEET写入。这样这个问题就得以解决了 二. 在这种大数据量的报表生成和导出中,要占用大量的内存,尤其是在使用TOMCAT的情况下,JVM最高只能支持到2G内存,则会发生内存溢出的情况。此时的内存开销 主要是两部分,一部分是该报表生成时的开销,另一部分是该报表生成后写入一个EXCEL时的开销。由于JVM的GC机制是不能强制回收的,因此,对于此种情形,我们要改变一种方式: 1. 将该报表设置起始行和结束行参数,在API生成报表的过程中,分步计算报表,比如一张20万行数据的报表,在生成过程中,可通过起始行和结束行分4-5次进行。这样,就 降低了报表生成时的内存占用,在后面报表生成的过程中,如果发现内存不够,即可自动启动JVM的GC机制,回收前面报表的缓存 2. 导出EXCEL的过程,放在每段生成报表之后立即进行,改多个SHEET页为多个EXCEL,即在分步生成报表的同时分步生成EXCEL,则通过 POI包生成EXCEL的内存消耗也得以降低。通过 多次生成,同样可以在后面EXCEL生成所需要的内存不足时,有效回收前面生成EXCEL时占用的内存 3. 再使用文件操作,对每个客户端的导出请求在服务器端根据SESSIONID和登陆时间生成唯一的临时目录,用来放置所生成的多个EXCEL,然后调用系统控制台,打包多个EXCEL为RAR 或者JAR方式,最终反馈给用户一个RAR包或者JAR包,响应客户请求后,再次调用控制台删除该临时目录。 4. 通过分段运算和生成,有效降低了报表从生成结果到生成EXCEL的内存开销。其次是通过使用压缩包,响应给用户的生成文件体积大大缩小,降低了多用户并 发访问时服务器下载文件的负担,有效减少多个用户导出下载时服务器端的流量,从而达到进一步减轻服务器负载的效果
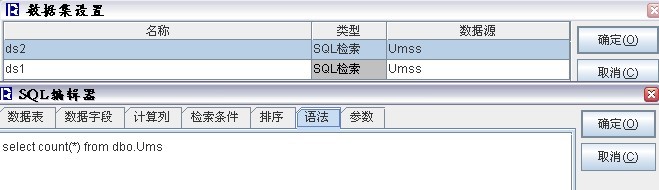
4. 程序部分 1.JSP里导出的链接格式:<a href=”<%=request.getContextPath()%>/exportToExcel.jsp?report=分页标签.raq&path=reportFiles\¶m=arg1=123,234;arg2=2″>导出Excel</a> 也可用javascript的方式 2.导出EXCEL中对于取最大行数,可以在报表里多定义一个数据集专门取最大行数,在后台通过API方式解析,保证通用性避免代码中出现SQL,复杂SQL,存储过程等,如图:
jsp具体代码: <%@ page contentType=”text/html;charset=GBK”%> <%@ page import=”com.runqian.report4.model.*”%> <%@ page import=”com.runqian.report4.usermodel.*”%> <%@ page import=”com.runqian.report4.view.excel.*”%> <%@ page import=”com.runqian.report4.util.*”%> <%@ page import=”java.util.ArrayList”%> <%@ page import=”java.io.*”%> <%@ page import=”java.sql.*”/> <html> <head> <title>导出EXCEL</title> </head> <body> <% request.setCharacterEncoding(“GBK”); String root = getServletContext().getRealPath(“/”); String path = request.getParameter(“path”); //相对路径 String report = request.getParameter(“report”); //报表名 String param = request.getParameter(“param”); //报表参数 String filePath = root + path + report; ReportDefine rd2 = (ReportDefine) ReportUtils.read(filePath);//读取报表 Context context = new Context(); // 获得报表定义中的数据集集合 DataSetMetaData dsmd = rd2.getDataSetMetaData(); // 取到需要修改的数据集对象 //SQL检索类型:SQLDataSetConfig //复杂SQL类型:CSQLDataSetConfig //存储过程类型:ProcDataSetConfig SQLDataSetConfig dsc = (SQLDataSetConfig) dsmd.getDataSetConfig(0); String sql = dsc.getSQL(); //连接数据库,查询查询有多少条记录 Connection conn = context.getConnectionFactory(“zHouHuiHui”) .getConnection(); ResultSet rs = null; Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); int num = 0; try { if (rs.next()) { num = rs.getInt(1); System.out.println(“条数:” + num); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null) rs.close(); if (stmt != null) stmt.close(); } int rowCount = 65536;//每页最大行数 int pageCount = 0; if (num % rowCount == 0) { pageCount = num / rowCount; } else { pageCount = num / rowCount + 1; } System.out.println(“总共多少页 :” + pageCount); try { for (int k = 0; k < pageCount; k++) { //读取报表模板 context = new Context(); ReportDefine rd = (ReportDefine) ReportUtils.read(filePath); //运算报表 //创建要导出的excel报表 ExcelReport excel = new ExcelReport(); //计算前,设置参数 ParamMetaData pmd = rd.getParamMetaData(); if (param != null && param.trim().length() != 0 && pmd != null) { String[] para = param.split(“;”); String[] pa = null; String paramName = “”; //参数名 String paramValue = “null”; //参数值 for (int i = 0; i < para.length; i++) { out.println(para[i]); pa = para[i].split(“=”); paramName = pa[0]; if (pa.length == 1) { paramValue = “”; context.setParamValue(paramName, paramValue); } else { if (pa[1].indexOf(“,”) == -1) { paramValue = pa[1]; context .setParamValue(paramName, paramValue); } else { ArrayList objArrayList = new ArrayList(); String[] b = pa[1].split(“,”); for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++) { objArrayList.add(b[j]); } context.setParamValue(paramName, objArrayList); } } } } context.setParamValue(“startRow”, 30000 * k); context.setParamValue(“endRow”, 30000 * (k + 1)); System.out.println(context.getParamValue(“startRow”)); System.out.println(context.getParamValue(“endRow”)); Engine enging = new Engine(rd, context); IReport iReport = enging.calc(); System.out.println(“[ToExcelServlet] – 运算报表结束!”); PrintSetup ps = iReport.getPrintSetup(); //取打印配置 ps.setPagerStyle(PrintSetup.PAGER_ROW); //设置报表分页方式为按数据行数分页 ps.setPaper((short) 0); //设置纸张类型 ps.setPaperWidth(1000); ps.setRowNumPerPage(65535); //设置按数据行数分页时每页的数据行数 iReport.setPrintSetup(ps); //设置打印配置*/ PageBuilder pb = new PageBuilder(iReport); //根据iReport中的PrintSetup里的信息进行分页 IReport[] ireports = pb.getAllPages(); //获得分页后的所有页集合 for (int i = 0; i < ireports.length; i++) { excel.export(ireports[i]); } excel.saveTo(“d://test//test” + k + “.xls”); } //将1个文件压缩成RAR格式 ExcelOutPut objRARFile = new ExcelOutPut(); int arg = objRARFile.RARFile(“d://test”, “d://test”, “”); OutputStream objOutputStream = response.getOutputStream(); response.setContentType(“application/octet-stream”); String httpHeader = “attachment;filename=report1.rar”; response.addHeader(“Content-Disposition”, httpHeader); FileInputStream infile = null;// 读取文件用 //生成对象用infile,准备读取文件 infile = new FileInputStream(“D://test.rar”); byte[] buffer = new byte[500]; int count = 0; count = infile.read(buffer); while (count > 0) { objOutputStream.write(buffer, 0, count); count = infile.read(buffer); } //ServletOutputStream sos = response.getOutputStream(); objOutputStream.close(); infile.close(); //以下两句必须要加,否则会报响应的输出流已经被占用 out.clear(); out = pageContext.pushBody(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } %> </body> </html> 3.将文件压缩成RAR格式,ExcelOutPut.java,具体代码: package com.runqian.report4.usermodel; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class ExcelOutPut { /* * * cmd 下调试成功的命令 * * 压缩:Rar a c:\test.rar c:\3Out_20050107.MDB * * 解压:UnRar x * c:\test.rar d:\ * */ private static String rarCmd = “C://Program Files//WinRAR//Rar.exe a “; private static String unrarCmd = “C://Program Files//WinRAR//UnRar x “;
private static int count = 0; /** * * 将1个文件压缩成RAR格式 * * rarName 压缩后的压缩文件名(不包含后缀) * * fileName 需要压缩的文件名(必须包含路径) * * destDir 压缩后的压缩文件存放路径 * return 0 表示压缩完成 * * 1 表示由于一些原因失败 * * * @throws IOException * * @throws InterruptedException * */ public static int RARFile(String rarName, String fileName, String destDir) { rarCmd += destDir + rarName + “.rar ” + fileName; String readStr = “”; try { System.out.println(“正在压缩文件…” + rarName + “.rar “); String s; Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(rarCmd); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(p.getInputStream())); while ((s = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) System.out.println(s); try { p.waitFor(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(rarCmd); System.out.println(“finished rar the file: ” + fileName); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return 1; } return 0; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub // ExcelOutPut objRARFile = new ExcelOutPut(); // objRARFile.RARFile(“d://test”, “d://test”, “”); int count = 199999; // 记录数 count = count / 30000 + 1; System.out.println(count); } } 5. 总结 1. 该问题本身并不是润乾报表运算或者生成时有内存溢出BUG,而是WEB容器本身的问题和JVM本身的机制问题 2. 经过外部API改造,可以使用方法对问题进行规避 3. 该案例具有一定的通用性,完全可以做成一个独立的大报表导出的功能,将大数据量的报表分段运算成多个EXCEL,PDF或者WORD,通过外部程序进行压缩处理,响应给用户压缩包 4. 该需求本身合理性值得斟酌,但存在就是合理,也需要客户的配合,让步最终导致了该问题的解决